Grey Body : 회색체
흑체와 달리 회색체(gray body)는 최대 흡수 능력을 가지지는 않지만, 그 외의 특성은 흑체와 유사합니다.
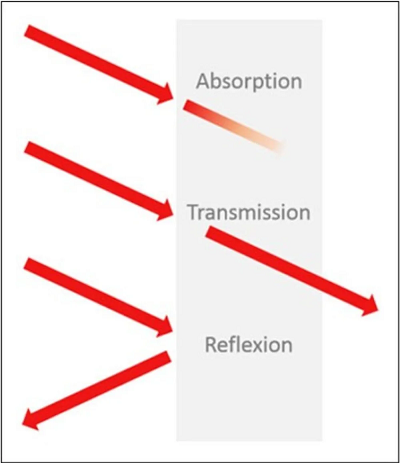
전자기 복사는 물질과 세 가지 방식으로 상호작용할 수 있습니다. 환경으로 반사되거나 확산 산란될 수 있고, 투명한 물체를 통해 투과될 수도 있으며, 물질 내부로 흡수될 수도 있습니다. 실제 상황에서는 이들 상호작용 중 하나가 غالب적으로 지배적인 경우가 많습니다. 에너지 보존 법칙에 따르면 흡수율(α), 반사율(ρ), 투과율(τ)의 합은 100%가 되어야 하며, 즉 1 = α + ρ + τ 입니다.
일반적으로 이 세 가지 파라미터는 파장과 물체 온도에 따라 달라집니다. 회색체는 α, ρ, τ가 상수이며 α가 1이 아닌 물체를 가정한 물리적 모델입니다. 따라서 특정 파장에서 결정된 방사율은 다른 모든 파장에서도 유효하다는 특성을 갖습니다.
실제 물질에서는 이 모델에 대한 근사만 존재합니다. 적절한 코팅을 사용하는 경우, 제한된 온도 범위와 분광 범위 내에서는 빛–물질 상호작용의 파라미터들을 상수로 가정할 수 있습니다.
In contrast to a black body, a gray body does not have a maximum absorption capacity, but otherwise has similar properties.
Electromagnetic radiation can interact with matter in three ways. It can be reflected or diffusely scattered back into the environment, transmitted by transparent objects, or absorbed in matter. In practical cases, one of these interactions often dominates. The law of conservation of energy requires that the sum of absorption (α), reflectivity (ρ), and transmissivity (τ) is equal to 100% or 1 = α + ρ + τ.
In general, all three parameters depend on the wavelength and object temperature. A Grey Body is a physical model for an object where α, ρ, and τ are constants and α is not equal to 1. It also follows that an emissivity determined for one wavelength is valid for all other wavelengths.
In practice, there are only approximations to this model. When using appropriate coatings, the parameters of the light-matter interaction can be assumed to be constants, at least within a limited temperature and spectral range.


