Focal Length : 초점 거리
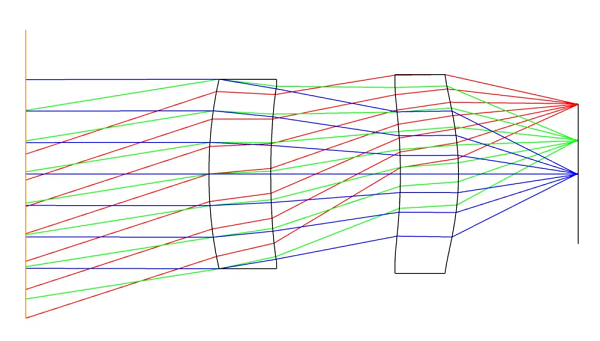
초점거리(focal length)는 광학 시스템의 굴절 능력을 설명하는 핵심적인 지표로, 광학계의 주평면과 초점 사이의 거리를 의미합니다. 이 값은 빛을 집속하는 시스템의 능력과 반비례 관계에 있습니다. 초점거리는 조리개 직경과 함께 광학 시스템의 F-넘버를 결정하며, 렌즈 구성에 대한 종합적인 설명을 제공합니다.
온도 측정의 관점에서 보면, 긴 초점거리는 고온계나 열화상 카메라의 측정 범위를 확장해 주어, 먼 거리에서도 대상 물체를 높은 광학 해상도로 정밀하게 분해할 수 있게 합니다. 동일한 측정 거리를 유지한 상태에서 측정 장비의 초점거리를 늘리면 측정 정확도는 향상됩니다. 그러나 열악한 환경 조건이나 접근성의 제약으로 인해 측정 거리를 충분히 짧게 확보하지 못하는 경우도 있을 수 있습니다.
초점거리를 늘리면 광학 해상도 또는 D:S 비가 향상되어 측정 스폿 크기가 더 작아지며, 작은 표적에 대해서도 온도 측정이 가능해집니다. 긴 초점거리와 짧은 측정 거리를 결합하면 측정 대상에 대한 현미경 수준의 관찰도 수행할 수 있습니다. 배율이 1보다 큰 광학계는 픽셀 크기 수준의 표적 크기에 대해 광학적 해상도를 제공합니다. 미세 스케일의 표적을 측정할 때에는 검출기 측의 F-넘버(또는 영상 수치 개구, image numerical aperture)뿐만 아니라, 물체 측의 수치 개구(numerical aperture)도 함께 고려해야 합니다.
일반적으로 초점거리가 길어질수록 장비의 크기도 커집니다. 이것이 망원 광학계가 광각 광학계에 비해 더 크고 부피가 큰 이유입니다. 초점거리는 측정 장비의 시야각(FOV)과 직접적으로 연결되어 있습니다. 짧은 초점거리는 넓은 FOV를 형성하여, 넓은 영역을 한눈에 파악할 수 있는 대면적 모니터링에 적합합니다.
그러나 FOV는 초점거리뿐만 아니라 센서 크기에도 의존합니다. 따라서 열화상 카메라를 다룰 때에는 이러한 파라미터들을 함께 고려할 필요가 있습니다. 픽셀 크기가 점점 작아지는 추세에 따라, 더 작은 센서로도 동일한 시야각을 유지하면서 더 짧은 초점거리를 적용할 수 있게 되었고, 이를 통해 장비를 더욱 소형화하고 경량화할 수 있습니다.
The focal length is a crucial measure in optics as it describes the refractive power of a system. It signifies the distance between the principal plane of the optics and the focal point. This measurement is inversely related to the system’s ability to focus light. Together with the aperture diameter, the focal length determines the F-number of an optical system, providing a comprehensive description of the lens configuration.
In the context of temperature measurement, a long focal length improves the range of a pyrometer or thermal imaging camera, enabling precise optical resolution of a target at a long distance. Maintaining the same distance and increasing the focal length of the measuring device increases the accuracy of the measurement. However, harsh environments or limited accessibility may hinder achieving a short measurement distance.
Increasing the focal length improves the optical resolution or D:S ratio, resulting in a smaller measurement spot and allowing temperature measurement of small targets. A large focal length combined with short distances enables microscopic inspection of the measurement object. Optics with a magnification larger than one provide optical resolution of target sizes in the dimension of the pixel size. When measuring micro-scale targets, the numerical aperture of the object side must be considered in addition to the F-number (or image numerical aperture) of the detector side.
Generally, as the focal length increases, so does the size of the instrument. This explains why telephoto optics are bulkier compared to wide-angle optics. The focal length is directly linked to the field of view (FOV) of the measurement device. A short focal length produces a wide FOV and provides large-area monitoring for a quick overview.
However, the FOV depends not only on the focal length but also on the sensor size. This makes it necessary to consider these parameters in combination when dealing with thermography cameras. With the trend towards decreasing pixel sizes, smaller sensors can accommodate shorter focal lengths with the same field of view, enabling the development of more compact and lighter devices.


