Field of View (FOV) : 시야각 (FOV)
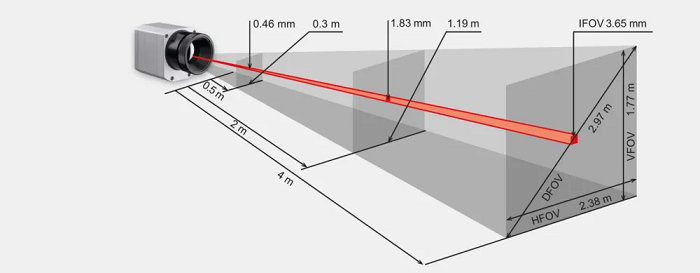
기기의 시야각(Field of View, FOV)은 장비가 목표 물체를 감지할 수 있는 각도 범위를 의미합니다. 고온계(pyrometer)의 경우, FOV는 흔히 온도계의 측정 스폿 크기로 설명됩니다. 열화상 분야에서는 카메라의 FOV가 카메라로 영상화할 수 있는 장면의 관측 영역을 결정합니다.
카메라의 FOV는 일반적으로 도(degree) 단위로 표현되며, 열화상 카메라의 광학계 구성과 검출기 크기에 따라 달라집니다. 이는 센서 크기와 카메라 광학계의 초점거리 f 간의 비율로 정의되며 다음과 같이 나타낼 수 있습니다.
FOV = 2 · arctan(센서 크기 / 2f) ≈ 센서 크기 / f
센서 포맷에 따라 FOV는 수평 시야각(HFOV)과 수직 시야각(VFOV)으로 표현할 수 있으며, 이 두 값으로부터 대각 시야각(DFOV)이 결정됩니다.
FOV의 선택은 종종 대상 물체까지의 거리에 의해 결정됩니다. 장거리 응용 분야에서는 좁은 FOV(망원 광학계, Tele-Optics)를 선택할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 먼 거리에서도 작은 물체를 감지할 수 있습니다. 짧은 거리에서 좁은 FOV를 사용하는 것도 가능하며, 이 경우 대상의 높은 확대 효과를 얻을 수 있습니다. 보다 고급 응용 분야에서는 8 µm–14 µm 파장 대역에서도 작은 물체를 감지하기 위해 현미경 광학계가 필요합니다.
넓은 FOV는 열화상 카메라가 더 넓은 영역을 한 번에 포착할 수 있게 해주어, 일반적인 감시나 광범위한 영역의 온도 분포를 신속하게 파악하는 데 유리합니다. 전기 설비 점검이나 대규모 환경 모니터링과 같은 경우에는 넓은 FOV가 특히 유리합니다.
작은 물체의 온도를 정확하게 측정하기 위해서는 FOV뿐만 아니라 공간 해상도, 즉 순간 시야각(IFOV)도 함께 고려해야 합니다. IFOV는 센서 어레이에서 하나의 픽셀에 해당하며, 구분 가능한 최소 물체 크기를 결정합니다. 정확한 온도 측정을 위해서는 측정 대상의 크기가 IFOV보다 커야 합니다. 일반적으로 물체의 크기는 최소한 3×3 픽셀에 해당해야 하며, 이를 측정 시야각(MFOV, Measurement Field of View)이라고 합니다.
FOV 계산기를 사용하면 카메라와 광학계 정보를 입력하여 HFOV, VFOV, IFOV, MFOV와 같은 필요한 FOV 데이터를 확인할 수 있습니다. 열화상 카메라에서 FOV의 선택은 카메라의 광학 해상도와 밀접하게 연관되어 있는데, 이는 작은 세부 사항을 얼마나 잘 구분할 수 있는지를 의미합니다. 광학 해상도가 높은 카메라는 더 미세한 디테일을 분해할 수 있어, 작은 물체나 먼 거리에 있는 대상을 관찰할 때 특히 중요합니다. 이러한 광학 해상도는 일반적으로 시야각이 좁은 카메라에서 더 높게 나타나므로, FOV와 광학 해상도 간의 절충 관계는 열화상에서 중요한 고려 사항이며, 이는 열화상 결과의 품질과 활용성 모두에 영향을 미칩니다.
The field of view (FOV) of an instrument refers to the angle at which the device can detect the target object. For pyrometers, the FOV is often described as the measurement spot size of the thermometer. In thermography, the FOV of a camera determines the observable area of a scene that can be imaged by the camera.
The camera FOV is typically expressed in degrees and depends on the configuration of optics and detector size of the thermal imaging camera. It’s defined by the ratio of the sensor size and the focal length f of the camera optics:
FOV=2⋅arctan(sensorsize2f)≈sensorsizef
.
With the sensor format, the FOV can be expressed as a horizontal field of view (HFOV) and a vertical field of view (VFOV). These two values result in the diagonal of the field of view (DFOV).
The choice of the FOV is often determined by the object’s distance. For long-range applications, a narrow FOV (Tele-Optics) can be selected, enabling the detection of small objects even at long distances. The use of a narrow FOV at a short distance is also possible and results in high magnification of the target. For advanced applications, microscope optics are required to detect small objects, even in the 8 µm – 14 µm waveband.
A wide FOV allows the thermal imaging camera to capture a larger area, which can be beneficial for general surveillance and rapid assessment of temperature distribution over wide areas. For inspections of electrical installations or large-scale environmental monitoring, a wide FOV is advantageous.
In addition to FOV, the spatial resolution, or the instantaneous field of view (IFOV), must be considered for accurate temperature measurements of small objects. The IFOV represents one pixel of the sensor array and determines the smallest resolvable object size. For accurate temperature measurements, the target size must be larger than the IFOV. Typically, the size of objects must be at least the equivalent of 3×3 pixels, which defines the measurement field of view (MFOV).
The FOV calculator allows users to enter the camera/optics information and displays necessary FOV data such as HFOV, VFOV, IFOV, and MFOV. The selection of the FOV in thermography cameras is closely linked to the camera’s optical resolution, which refers to its ability to distinguish small details. A camera with high optical resolution can resolve finer details, critical when examining small or distant objects. This optical resolution is typically higher in cameras with narrower fields of view, so the trade-off between FOV and optical resolution is an important consideration in thermography, affecting both the quality and usability of the thermal imaging results.


