D:S : 거리 대 스폿 비율
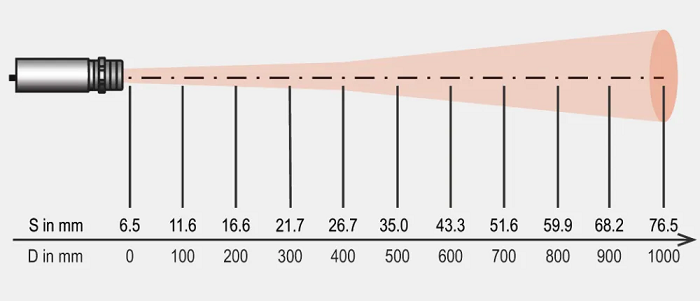
거리 대비 스폿 크기 비율(D:S 비율)은 온도계나 열화상 카메라와 같은 온도 측정 장비의 광학 해상도를 설명하는 데 널리 사용되는 지표입니다. 이는 측정 대상까지의 거리(초점 거리) D를 측정 스폿의 크기로 나누어 계산합니다. D:S 비율 값은 특정 거리에서 장비의 측정 스폿 크기를 판단하는 데 활용할 수 있습니다. 정확한 온도 측정을 위해서는 측정 대상의 크기가 최소한 측정 스폿 크기와 같아야 합니다. 이는 대상의 크기가 측정 스폿과 정확히 같을 경우, 측정 장비가 대상에서 방출되는 에너지의 최소 90% 이상을 감지하도록 보장하기 위함입니다.
초점 조절이 가능한 장비의 경우, 전체 측정 범위에 대해 하나의 D:S 비율이 적용됩니다. 거리가 멀어질수록 스폿 크기는 커지지만, 비율 자체는 일정하게 유지됩니다. 반면, 소형 파이로미터와 같은 고정 초점 장비에서는 특정 초점 거리에서만 D:S 비율이 제시됩니다. 측정 대상을 초점 위치에서 벗어나게 하면 D:S 비율이 감소하고, 그 결과 측정 스폿이 커지며 온도 측정 오차가 발생할 수 있습니다.
광학적인 관점에서 보면, D:S 비율은 측정 장비의 초점거리 F와 검출기 크기 d와 관련이 있습니다. 초점거리가 길수록 D:S 비율은 향상되지만, 일반적으로 장비의 크기 또한 커지게 됩니다. 소형 장비는 대체로 중간 수준의 D:S 비율을 가지며, 이는 측정 대상이 크고 전체 영역에 대해 평균 온도를 측정해야 하는 응용 분야에서 유용할 수 있습니다.
열화상 카메라에서는 최소 스폿 크기라는 개념이 일반적으로 사용됩니다. 검출기 어레이의 각 픽셀은 하나의 잠재적인 측정 스폿을 나타내며, 이는 순간 시야각(IFOV)을 정의합니다. 온도 측정에서 높은 정확도를 확보하기 위해서는 보통 하나 이상의 픽셀이 필요하며, 일반적으로 3×3 픽셀로 구성된 측정 시야각(MFOV)을 사용합니다. 이 MFOV는 파이로미터의 측정 스폿과 유사하며, 열화상 카메라에서도 D:S 비율을 계산할 수 있습니다.
The distance-to-spot size ratio (D:S ratio) is a widely used metric for describing the optical resolution of temperature measurement instruments, such as thermometers or thermography cameras. It is calculated by dividing the measurement distance (focal distance) D of the target by the measurement spot size. The D:S ratio value can be used to determine the measurement spot of the device at a specific distance. For highly accurate temperature measurement, the target size should be at least equal to the size of the measurement spot. This ensures that the measurement device detects at least 90% of the energy of the target if the target is exactly the size of the measurement spot.
In devices with adjustable focus, a single D:S ratio is applied for the full measurement range. Although the spot size increases with distance, the ratio remains constant. Conversely, in fixed focus devices, such as compact pyrometers, the D:S ratio is given only for a certain focal distance. Shifting the target out of focus decreases the D:S ratio, leading to a larger measurement spot and potential temperature deviations.
From an optics point of view, the D:S ratio is related to the focal length F and detector size d of the measurement device. A longer focal length results in an enhanced D:S ratio, but also typically leads to a larger dimension of the measurement device. Compact devices often have more moderate D:S ratios, which can be useful in applications where the target object is large and needs to be tested in its entirety, taking an average temperature measurement over the total size of the object.
For thermal imaging cameras, the concept of the minimum spot size is common. Each pixel out of the detector array represents a potential measurement spot, defining the instantaneous field of view (IFOV). High accuracy in temperature measurement often requires more than one pixel, capturing a measurement field of view (MFOV) usually encompassing 3×3 pixels. This MFOV is comparable to the measurement spot of a pyrometer, and the D:S ratio can also be calculated for thermography cameras.


