Bolometer : 볼로미터
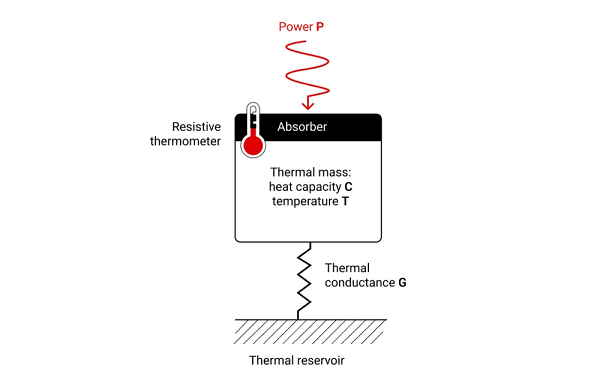
볼로미터(bolometer)는 저항 온도계의 원리를 이용해 복사를 측정하는 장치입니다. 복사가 흡수되면 가능한 한 흑화된 표면에서 열이 발생하며, 이로 인해 재료의 온도가 상승합니다. 이러한 온도 상승은 재료의 전기 저항 변화를 유발하고, 이 저항 변화는 전기적으로 측정할 수 있습니다. 반도체(서미스터)는 온도 계수가 매우 크기 때문에 검출기의 감도를 높일 수 있어 볼로미터 재료로 자주 사용됩니다. 온도가 알려진 히트 싱크와 정의된 열저항을 갖는 열 브리지를 구성하면, 복사를 연속적으로 측정할 수 있습니다. 오늘날에는 전자기 스펙트럼의 넓은 영역에서 높은 흡수율을 가지는 매우 얇은 코팅을 제작할 수 있게 되었으며, 이로 인해 볼로미터 검출기는 넓은 분광 범위의 적외선 복사를 감지하는 데 적합해졌습니다. 또한 여러 개의 볼로미터를 배열 형태로 구성하면, 적외선 복사를 영상으로 검출하는 장치인 적외선 카메라를 구현할 수 있습니다.
A bolometer is a device used to measure radiation based on a resistance thermometer. When radiation is absorbed, it causes heating on a surface that is as blackened as possible. This heating leads to a change in resistance in the material, which can be measured. Semiconductors (thermistors) are often used because their temperature coefficient is high, making the detector more sensitive. A thermal bridge with a defined thermal resistance to a heat sink of known temperature allows for continuous measurement of radiation. Nowadays, very thin coatings with a high absorption coefficient for a wide part of the electromagnetic spectrum can be produced, making bolometer detectors suitable for detecting infrared radiation over a wide spectral range. When multiple bolometers are combined to form an array, an imaging device for detecting infrared radiation, an infrared camera, can be built.


