Waveband : 파장대
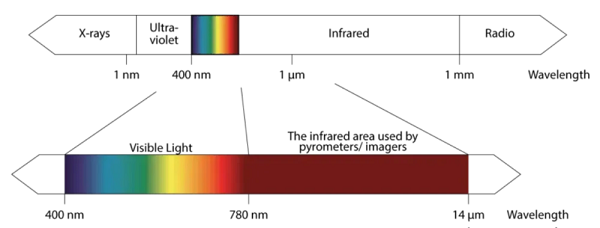
광학 및 영상에서 “스펙트럼 범위”라는 용어는 영상 시스템이나 센서가 민감하게 반응하는 전자기 스펙트럼의 특정 부분을 가리킵니다. 이 범위는 시스템이 감지하고 영상화에 사용할 수 있는 전자기파의 유형을 결정합니다. 이는 검출기의 감도, 대기 창(atmospheric windows), 응용의 온도 범위와 같은 요인에 의해 영향을 받습니다.
대부분의 온도 측정 응용에서 스펙트럼 범위는 가시광선에서 장파 적외선(LWIR) 대역까지 확장됩니다. 이는 방출원(emitting source)의 물리적 거동 때문입니다. 흑체(blackbody) 방출원의 온도는 그 방출 스펙트럼의 피크 파장과 관련이 있습니다. 빈의 변위 법칙(Wien’s displacement law)에 따르면 파장과 온도는 연결되어 있으므로, 방출원의 온도가 측정 장치에 적합한 파장 범위를 결정합니다. 열화상(thermal imaging), 특히 실온에서는 스펙트럼 범위가 LWIR 8 µm – 14 µm 대역으로 설정되며, 이 범위에서의 열 복사를 검출하는 데 효과적입니다.
스펙트럼 범위는 온도 범위에 의해서만 결정되는 것이 아니라 대기 창에 의해서도 영향을 받습니다. 예를 들어 공기에 의한 적외선 흡수는 복사가 대기를 통해 더 잘 통과할 수 있는 특정 파장대에 검출기를 제한합니다.
스펙트럼 범위를 이해하는 것은 효과적인 열화상 시스템을 설계하고 결과 영상을 해석하는 데 매우 중요합니다. 서로 다른 파장은 물체의 열적 특성에 대해 서로 다른 정보를 제공합니다. 적절한 스펙트럼 범위를 선택함으로써 열화상 기술자는 특정 응용에 맞춰 영상을 최적화할 수 있으며, 다양한 상황에서 열 관련 특성을 진단, 모니터링 및 관리하는 능력을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 이러한 선택적 민감성은 열화상술과 더 넓은 영상 기술의 기본적인 측면입니다.
The waveband or spectral range refers to a selected portion of the total electromagnetic spectrum, which spans from high-energy gamma rays to low-energy radio waves. For temperature measurement applications, this range typically includes the near-infrared, mid-infrared, and long-wave infrared bands.
In optics and imaging, the term “spectral range” denotes the specific part of the electromagnetic spectrum that an imaging system or sensor is sensitive to. This range determines the type of electromagnetic waves the system can detect and use for imaging. It is influenced by factors such as the sensitivity of the detector, atmospheric windows, and the temperature range of the application.
For most temperature measurement applications, the spectral range extends from the visible spectrum to the long-wave infrared (LWIR) band. This is due to the physical behavior of the emitting source. The temperature of a blackbody source is related to the peak wavelength of its emission spectrum. According to Wien’s displacement law, wavelength and temperature are connected, so the temperature of the source determines the appropriate wave range for the measuring device. For thermal imaging, particularly at room temperature, the spectral range is set to the LWIR 8 µm – 14 µm band, which is effective for detecting thermal radiation in this range.
The spectral range is not only determined by the temperature range but is also influenced by atmospheric windows. For instance, the absorption of infrared radiation by air restricts detectors to certain wavebands where the radiation can pass through the atmosphere more effectively.
Understanding the spectral range is crucial for designing effective thermal imaging systems and interpreting the resulting images. Different wavelengths provide distinct information about an object’s thermal properties. By selecting the appropriate spectral range, thermographers can tailor their imaging to specific applications, improving their ability to diagnose, monitor, and manage heat-related characteristics in various scenarios. This selective sensitivity is a fundamental aspect of thermography and broader imaging technologies.


