Short-wave Infrared (SWIR) : 단파장 적외선
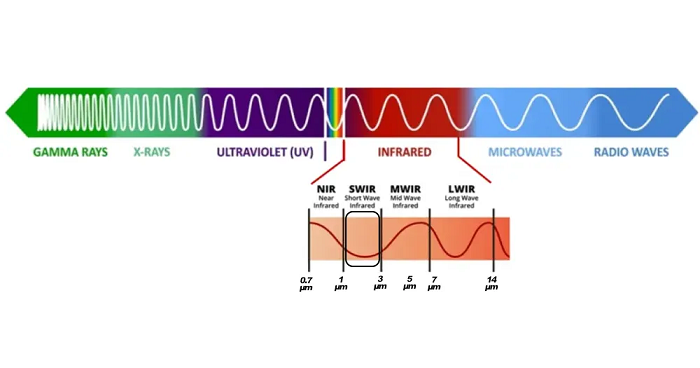
정의 및 스펙트럼 범위
단파장 적외선(SWIR) 카메라는 일반적으로 약 ~1.0 µm에서 1.7 µm 범위를 운용하는 적외선 영상 시스템으로, 일부 시스템은 2.5–3.0
µm까지 확장되기도 한다. NIR과 SWIR 사이의 파장 경계는 보편적으로 강제된 것이 없으며 제조업체가 전이를 다르게 정의할 수 있고 사양이 종종 겹친다. 실제로 명칭보다 응용 요구가 훨씬 더 중요하다.
영상 특성
주변 온도에서는 SWIR 카메라가 일반적인 열화상용으로 사용되는 경우는 거의 없다. 대신 반사된 빛과 방출된 복사를 검출하여 대비 기반 검사 작업에 매우 효과적이다. InGaAs 검출기 기술이 일반적으로 사용되며,
SWIR 대역 전반에 걸쳐 높은 감도와 낮은 잡음을 제공한다.
주요 응용 분야
- 반도체 및 웨이퍼 검사
단파적외선(SWIR) 카메라의 가장 확립된 응용 중 하나는 반도체 및 웨이퍼 검사입니다. 일반적으로 1000 nm에서
1400 nm 사이에서 동작하는 SWIR 시스템은 웨이퍼 대 웨이퍼 본딩 공정에서 기포, 균열 및 갇힌 공기층을 탐지하는 데 사용됩니다. 제어된 조명 하에서 SWIR 카메라는 가시광 카메라로는 보이지 않는 내부 결함을 식별하는 데 탁월한 콘트라스트를 제공합니다.
- 레이저 프로파일링 및 정렬
SWIR 카메라는 특히 약 1.06 µm 부근에서 동작하는 레이저의 프로파일링 및 정렬에도 널리 사용됩니다. 빔 형태, 출력 분포 및 정렬 정확도를 시각화할 수 있게 해줍니다. 높은 레이저 강도로부터 센서를 보호하기 위해 광학 필터링이 자주 필요합니다.
- 고온 산업 측정
고온 산업 환경에서 방사선 계측 보정된 SWIR 카메라는 대략 450 °C에서 1800 °C 범위의 비접촉 온도 측정을 가능하게 합니다. 응용 분야로는 용융 금속 처리, 주조, 단조 및 열처리가 포함됩니다. 단일 지점 광전온도계와 달리
SWIR 카메라는 전장(풀-필드)
열 데이터를 제공하여 운영자가 실시간으로 온도 균일성과 공정 안정성을 평가할 수 있게 합니다.
- 금속 적층 제조(3D
프린팅)
SWIR 카메라는 용융 풀 온도, 열 구배, 냉각 속도 및 레이저 안정성을 모니터링하는 데 점점 더 중요해지고 있습니다. 스팟 기반 센서와 비교할 때 SWIR 이미징은 공간적으로 분해된 온도 데이터를 제공하여 공정 제어, 기계적 특성 및 부품 품질 향상을 지원합니다. 특수 시스템은 종종 인쇄 공정에 맞춘 레이저 차단 필터를 통합합니다.
선택 시 고려사항
SWIR 카메라를 평가하는 엔지니어는 다음 사항을 고려해야 합니다:
- 스펙트럼 범위
- 교정 요구사항
- 레이저 노출
- 검출기 재료
- 공간 해상도
- 광학 구성
Definition and Spectral Range
Short-Wave
Infrared (SWIR) cameras are infrared imaging systems that operate over a
spectral range typically spanning ~1.0 µm to 1.7 µm, with
some systems extending to 2.5–3.0 µm. There is no universally
enforced wavelength boundary between NIR and SWIR; manufacturers may define the
transition differently, and specifications often overlap. In practice,
application requirements are far more important than nomenclature.
Imaging Characteristics
At
ambient temperatures, SWIR cameras are generally not used for conventional
thermal imaging. Instead, they detect reflected light and emitted radiation,
making them highly effective for contrast-driven inspection tasks. InGaAs
detector technology is commonly used, offering high sensitivity and low noise
across the SWIR band.
Key Applications
- Semiconductor and Wafer Inspection
One of
the most established applications for SWIR cameras is semiconductor and wafer
inspection. Operating typically between 1000 nm and 1400 nm, SWIR
systems are used to detect voids, cracks, and trapped air layers in
wafer-to-wafer bonding processes. With controlled illumination, SWIR cameras
provide exceptional contrast for identifying internal defects that are
invisible to visible cameras.
- Laser Profiling and Alignment
SWIR
cameras are also widely used for laser profiling and alignment, particularly
for lasers operating near 1.06 µm. They enable visualization of
beam shape, power distribution, and alignment accuracy. Optical filtering is
frequently required to protect sensors from high laser intensities.
- High-Temperature Industrial Measurement
In
high-temperature industrial environments, radiometrically calibrated SWIR
cameras enable non-contact temperature measurement from approximately 450 °C to 1800 °C.
Applications include molten metal handling, casting, forging, and heat
treatment. Unlike single-point pyrometers, SWIR cameras provide full-field
thermal data, allowing operators to assess temperature uniformity and process
stability in real time.
- Metal Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
SWIR cameras are increasingly critical in metal additive manufacturing, where they are used to monitor melt pool temperature, thermal gradients, cooling rates, and laser stability. Compared to spot-based sensors, SWIR imaging delivers spatially resolved temperature data that supports improved process control, mechanical properties, and part quality. Specialized systems often incorporate laser-blocking filters tailored to the printing process.
목록으로


